Projects
Multifunctional Bio-inspired Nanoparticles
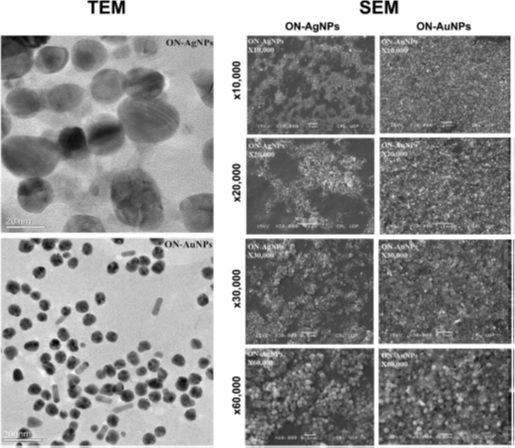
Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles is clean, safe, energy redeemable and environment friendly process. Biogenic nanoparticles have diverse applications in biomedical, industrial, agriculture and environmental sectors and we have conducted various research studies in this niche. Phytochemicals offer immense promise for sustainable development and production of nanotechnology-enabled products. In one of our study, Olax nana Wall. ex Benth. (family: Olacaceae) aqueous extract was used as an effective stabilizing agent to produce biogenic silver (ON-AgNPs) and gold nanoparticles (ON-AuNPs), which were investigated for biocompatibility and prospective biomedical applications (antibacterial, anticancer, antileishmanial, enzyme inhibition, antinociceptive, and anti-inflammatory activities). Various characterization techniques (XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, DLS, EDX, and SAED) revealed efficient biosynthesis of ON-AgNPs (26 nm) and ON-AuNPs (47 nm). In the toxicological assessment, ON-AgNPs and ON-AuNPs were found biocompatible towards human RBCs and macrophages (IC50 > 200 μg/mL). In a concentration range of 62.5-2000 μg/mL, a strong antibacterial effect was produced by ON-AgNPs against Staphylococcus epidermidis (MIC = 7.14 μg/mL) and Escherichia coli (8.25 μg/mL), while ON-AuNPs was only active against Staphylococcus aureus (9.14 μg/mL). At a concentration of 3.9-500 μg/mL, a dose-dependent inhibition of HepG2 cancer cells was produced by ON-AgNPs (IC50 = 14.93 μg/mL) and ON-AuNPs (2.97 μg/mL). Both ON-AgNPs and ON-AuNPs were found active against Leishmania tropica (KMH23) promastigotes (IC50 = 12.56 and 21.52 μg/mL) and amastigotes (17.44 and 42.20 μg/mL), respectively, after exposure to a concentration range of 1-200 μg/mL for 72 h. Preferential enzyme inhibition against urease and carbonic anhydrase II were noted for ON-AgNPs (39.23 and 8.89 %) and ON-AuNPs (31.34 and 6.34 %), respectively; however, these were found inactive against xanthine oxidase at 0.2 mg/mL. In the in vivo antinociceptive (acetic acid-induced abdominal constrictions) and anti-inflammatory (carrageenan-induced paw edema) activities, ON-AgNPs and ON-AuNPs at doses of 40 and 80 mg/kg, significantly attenuated the tonic nociception (P < 0.001) and ameliorated the carrageenan-induced inflammation (P < 0.01, P < 0.001). The results of in vitro and in vivo activities indicated that the biogenic nanoparticles can be used as valuable theranostic agents for further exploration of diverse biomedical applications. [Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018]
We also have performed Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) mediated synthesis of other metal oxide nanoparticles (ZnO, NiO, Fe2O3, Co3O4 and PbO) and tested for diverse biological applications and toxicological assessments.[Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 2017]; [Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2017]; [Nanomedicine, 2017]; [Artificial Cells, 2017]; [Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2017]; [Journal of Interdisciplinary Nanomedicine, 2017]. Furthermore, in vitro cholinesterase enzymes inhibitory potential and in silico molecular docking studies of biogenic metal oxides nanoparticles were performed. [Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic Metal-Organic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 2019]
Designing Stimuli‐Responsive Upconversion Nanoparticles that Exploit the Tumor Microenvironment
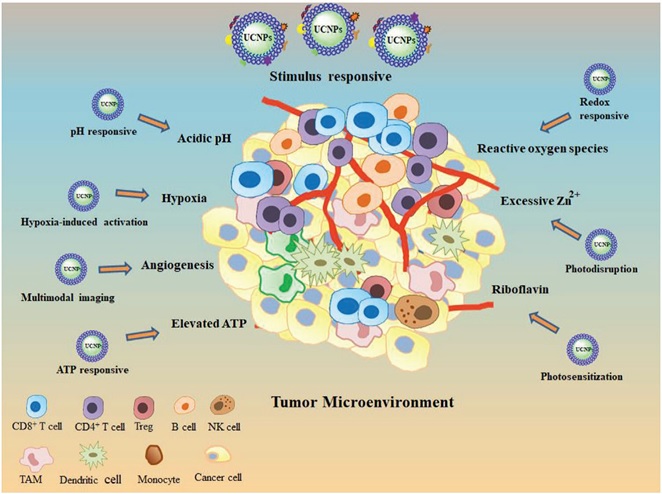
Tailoring personalized cancer nanomedicines demands detailed understanding of the tumor microenvironment. In recent years, smart upconversion nanoparticles with the ability to exploit the unique characteristics of the tumor microenvironment for precise targeting have been designed. To activate upconversion nanoparticles, various bio‐physicochemical characteristics of the tumor microenvironment, namely, acidic pH, redox reactants, and hypoxia, are exploited. Stimuli‐responsive upconversion nanoparticles also utilize the excessive presence of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), riboflavin, and Zn²⁺ in tumors. The design of stimulus‐responsive upconversion nanoparticles that precisely target and respond to tumors via targeting the tumor microenvironment and intracellular signals is desired. Detailed understanding of the tumor microenvironment and the personalized design of upconversion nanoparticles will result in more effective clinical translation. [Advanced Materials, 2020]
Phage Capsid Nanoparticles as Multivalent Inhibitors of Viral Infections
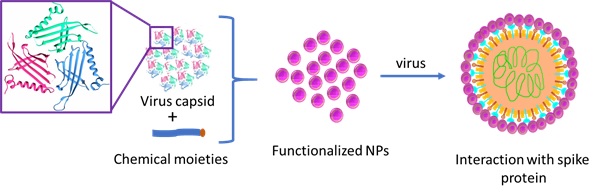
In the present time, coronavirus disease COVID-19 has become prevalent across the globe and declared as a pandemic by the world health organization (WHO). As of now, many vaccines and medicines are in the approval process or at different stages of preclinical investigations to coup with the COVID-19. Coronavirus has a spike protein, which tends to bind with receptors present in the lung tissues, and that helps in its entry to the cells and replication inside. Therefore, we are in need to design the multivalent nanomaterials, which can act as receptors to bind with spike protein of virus and stop its replication. [Science Bulletin, 2020]
Tailoring Nanomaterials for Targeting Tumor‐Associated Macrophages
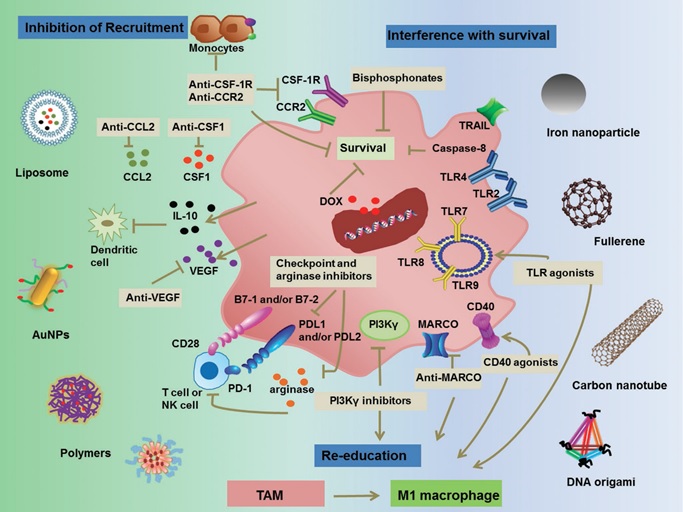
Advances in the field of nanotechnology together with an increase understanding of tumor immunology have paved the way for the development of more personalized cancer immuno‐nanomedicines. Nanovehicles, due to their specific physicochemical properties, are emerging as key translational moieties in tackling tumor‐promoting, M2‐like tumor‐associated macrophages (TAMs). Cancer immuno‐nanomedicines target TAMs primarily by blocking M2‐like TAM survival or affecting their signaling cascades, restricting macrophage recruitment to tumors and re‐educating tumor‐promoting M2‐like TAMs to the tumoricidal, M1‐like phenotype. We have developed several biofunctionalized TAMs targeting nanomedicines which are employed in combination with radio, chemo and immunotherapy. Furthermore, imaging TAMs with nanoparticles so as to forecast a patient’s clinical outcome, describing treatment options, and observing therapy responses are our key targets. [Advanced Materials, 2019]; [Science China-Chemistry, 2018]
Detection of Enzyme Triggered Peptide Self-Assembly
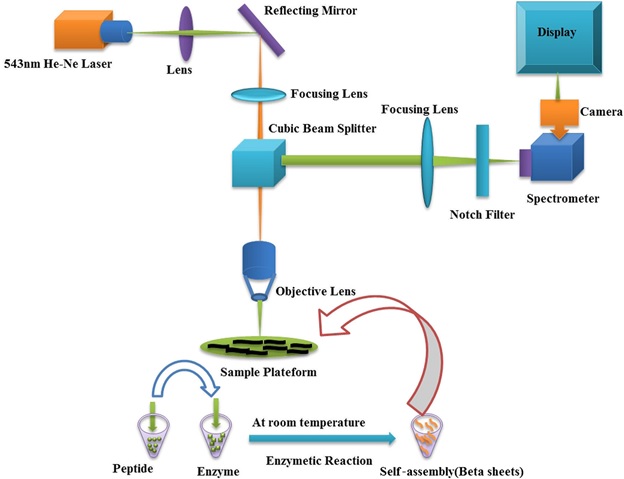
Vibrational spectroscopy of peptides and peptides based self-assembled macromolecules play key role in early stage detection of cancerous and viral diseases. We provide here a rapid and accurate trace detection system for enzyme triggered peptide self-assembly by taking a snapshot of peptide nanostructures to identify specific domains based on amino acid vibrational bands. The Enzyme triggered peptides present in both aqueous solution and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells were excited by a laser line of 543 nm while intensities of Raman bands were recorded from 500–1800 cm-1. The spectra consisted of several well resolved peaks located at 655 cm-1, 1081 cm-1 and 1670 cm-1 for peptide, while 834 cm-1, 851 cm-1,896 cm-1 and 915 cm-1 for enzyme, indicating vibrational bands of their functional groups. Raman signatures at 768 cm-1, 1144 cm-1, 1297 cm-1 , 1305 cm-1, 1571 cm-1 appeared in case of self-assembled peptides at new positions, indicating the presence of highly stable secondary structure of beta sheets. We detected 0.78 µg/mL as limit of detection for peptide self-assembly with Laser Confocal Raman Microscopy in aqueous solution. These self-assembled nano-machines in cellular environment can be used to monitor and regulate the cellular processes for the diagnosis of biological diseases incorporated with our label free Laser Confocal Raman Microscopy methodology. [Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2020]. Furthermore, in another related project we have optically characterized and monitored enzyme catalyzed short chain peptides in cellular environment. [Catalysis Letters, 2020]
Analytical Characterization of Nanoparticle-protein Corona
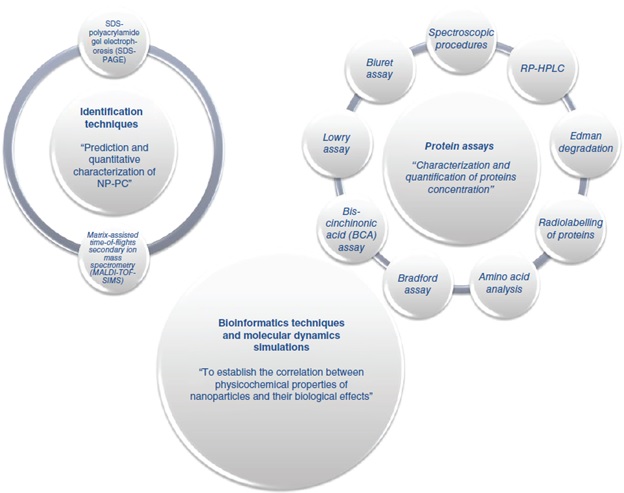
In spite of radical advances in nanobiotechnology, the clinical translation of nanoparticle (NP)-based agents is still a major challenge due to various physiological factors that influence their interactions with biological systems. Recent decade witnessed meticulous investigation on protein corona (PC) that is the first surrounds NPs once administered into the body. Formation of PC around NP surface exhibits resilient effects on their circulation, distribution, therapeutic activity, toxicity and other factors. Although enormous literature is available on the role of PC in altering pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of NPs, understanding on its analytical characterization methods still remains shallow. The impact of PC on biological fate of NPs and analytical methods employed for studying the NP-PC are vital to be explored. [Nanomedicine, 2020]
Fabrication of Poly (butadiene-block-ethylene oxide) Based Amphiphilic Polymersomes: An Approach for Improved Oral Pharmacokinetics of Sorafenib
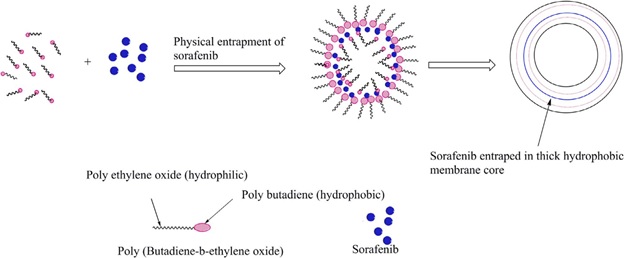
Sorafenib (SFN), a hydrophobic anticancer drug, has several limitations predominantly poor aqueous solubility and hepatic first-pass effect, limiting its oral delivery that results into several other complications. We have developed Sorafenib loaded polymersomes using poly butadiene block poly ethylene oxide (PB-b-PEO), an amphiphilic co-block polymer. Prior to drug loading, critical aggregate concentration (CAC) of polymer was calculated for stable formulation synthesis. The developed SFN loaded PB-b-PEO polymersomes (SFN-PB-b-PEO, test formulation) characterized by DLS and cryo-TEM showed particle size 282 nm, polydispersity (PDI) of less than 0.29 and membrane thickness of about 20 nm. SFN-PB-b-PEO polymersomes demonstrated encapsulation efficiency of 71 % and showed sustained drug release up to 144 h. Formulation remained stable for 3 months in suspension form. In vitro cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells showed 1.7 folds improved toxicity compared to SFN suspension. In addition, oral administration of SFN-PB-b-PEO polymersomes in BALB/c mice showed increased Cmax and AUC0–96 by 1.7 and 2.77-fold respectively (p < 0.05) compared to those of SFN suspension (reference formulation). Findings suggest that the SFN-PB-b-PEO polymersomes can be a potential candidate for oral delivery of SFN. [International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2018]; [International Journal of Polymeric Materials, 2018]
Stable and Reproducible Synthesis of Gold Nanorods for Biomedical Applications
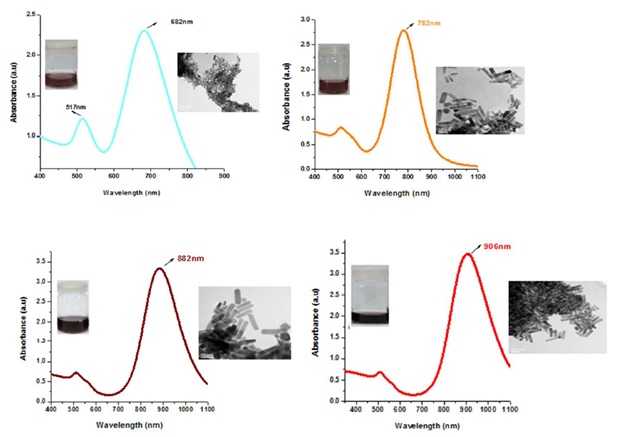
UV-Vis absorption spectra of GNRs from shorter (682 nm) to longer (906 nm) LSPR. TEM images show mono-disperse population with high yield.
Gold nanorods (GNRs) are ideal choice in biomedical research due to their amenability of synthesis, tunable plasmonic properties, less toxicity and ease of detection but their diverse biological applications necessitate stable structure. Despite two decades efforts made towards reproducible anisotropic structures synthesis, still we have not achieved kinetic control during GNRs growth. Current study is an attempt to apprehend thermodynamic and kinetic parameters for synthesizing mono-disperse, reproducible and highly stable GNRs with desired aspect ratios. Effects of various growth parameters and assay steps on the facile and reproducible synthesis of GNRs are analyzed. GNRs environmental and biological colloidal stability is studied through UV-vis spectroscopy based particle instability parameter (PIP60°C) and alkaline pH can trigger colloidal instability. GNRs remain stable at higher salt concentration, physiological and slightly acidic pH. GNRs can be stored in 0.001 M CTAB for 03 months without compromising their stability. PEGylated GNRs are quite stable in cellular media solution (PIP <0.1). With current optimized growth conditions, no aggregation at physiological pH and stability at high temperatures make GNRs an ideal candidate in biomedical applications. [IET Nanobiotechnology, 2017]; [Nano Today, 2018]
Anti-Alzheimer's Studies on β-Sitosterol Isolated from Polygonum hydropiper L
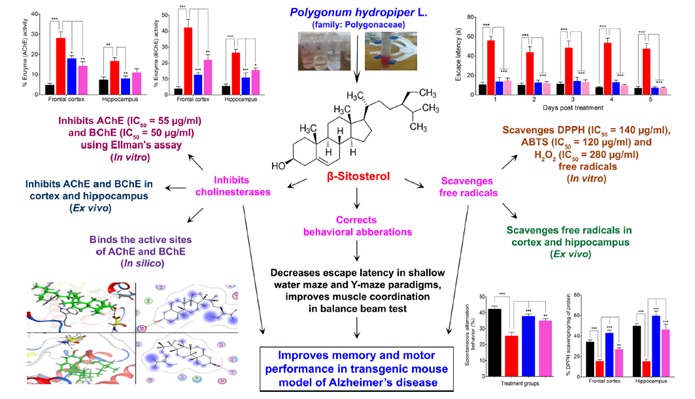
The family Polygonaceae is known for its traditional use in the management of various neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In search of new anti-AD drugs, β-sitosterol isolated from Polygonum hydropiper was subjected to in vitro, in vivo, behavioral and molecular docking studies to confirm its possibility as a potential anti-Alzheimer’s agent. The in vitro AChE, BChE inhibitory potentials of β-sitosterol were investigated following Ellman’s assay. The antioxidant activity was tested using DPPH, ABTS and H2O2 assays. Behavioral studies were performed on a sub-strain of transgenic mice using shallow water maze (SWM), Y-maze and balance beam tests. β-sitosterol was tested for in vivo inhibitory potentials against cholinesterase’s and free radicals in the frontal cortex (FC) and hippocampus (HC). The molecular docking study was performed to predict the binding mode of β-sitosterol in the active sites of AChE and BChE as inhibitor. Considerable in vitro and in vivo cholinesterase inhibitory effects were observed in the β-sitosterol treated groups. β-sitosterol exhibited an IC50 value of 55 and 50 μg/mL against AChE and BChE respectively. Whereas, the activity of these enzymes were significantly low in FC and HC homogenates of transgenic animals. Molecular docking studies also support the binding of β-sitosterol with the target enzyme and further support the in vitro and in vivo results. In the antioxidant assays, the IC50 values were observed as 140, 120, and 280 μg/mL in the DPPH, ABTS and H2O2 assays respectively. The free radicals load in the brain tissues was significantly declined in the β-sitosterol treated animals as compared to the transgenic-saline treated groups. In the memory assessment and coordination tasks including SWM, Y-maze and balance beam tests, β-sitosterol treated transgenic animals showed gradual improvement in working memory, spontaneous alternation behavior and motor coordination. These results conclude that β-sitosterol is a potential compound for the management of memory deficit disorders like AD. [Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2017]; [Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2019]
HPLC-DAD Finger Printing, Antioxidant, Cholinesterase, and α-glucosidase Inhibitory Potentials of a Novel Plant Olax nana

Snapshot of Olax nana plant at collection point
The medicinal importance of a novel plant Olax nana Wall. ex Benth. (family: Olacaceae) was revealed for the first time via HPLC-DAD finger printing, qualitative phytochemical analysis, antioxidant, cholinesterase, and α-glucosidase inhibitory assays. The crude methanolic extract of O. nana (ON-Cr) was subjected to qualitative phytochemical analysis and HPLC-DAD finger printing. The antioxidant potential of ON-Cr was assessed via 1,1-diphenyl,2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2-azinobis[3-ethylbenzthiazoline]-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) free radical scavenging assays. Furthermore, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) & butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities were performed using Ellman’s assay, while α- glucosidase inhibitory assay was carried out using a standard protocol. The qualitative phytochemical analysis of ON-Cr revealed the presence of secondary metabolites like alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, sterols, saponins and terpenoids. The HPLC-DAD finger printing revealed the presence of 40 potential compounds in ON-Cr. Considerable anti-radical activities was revealed by ON-Cr in the DPPH, ABTS and H2O2 free radical scavenging assays with IC50 values of 71.46, 72.55 and 92.33 μg/mL, respectively. Furthermore, ON-Cr showed potent AChE and BChE inhibitory potentials as indicated by their IC50 values of 33.2 and 55.36 μg/mL, respectively. In the α-glucosidase inhibition assay, ON-Cr exhibited moderate inhibitory propensity with an IC50 value of 639.89 μg/mL. This study investigated Olax nana for the first time for detailed qualitative phytochemical tests, HPLC-DAD finger printing analysis, antioxidant, anticholinesterase and α-glucosidase inhibition assays. The antioxidant and cholinesterase inhibitory results were considerable and can provide scientific basis for further studies on the neuroprotective and anti-Alzheimer’s potentials of this plant. ON-Cr may further be subjected to fractionation and polarity guided fractionation to narrow down the search for isolation of bioactive compounds. [BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018]. We also have performed detailed assessment of plant species such as Atriplex lasiantha Boiss, Dysphania ambrosioides L and Polygonum hydropiper L. [BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2019]. [Natural Product Research, 2018]. [BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2016].
The Absence of HCV RNA and NS5A Protein in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells is a Prognostic Tool for Sustained Virological Response
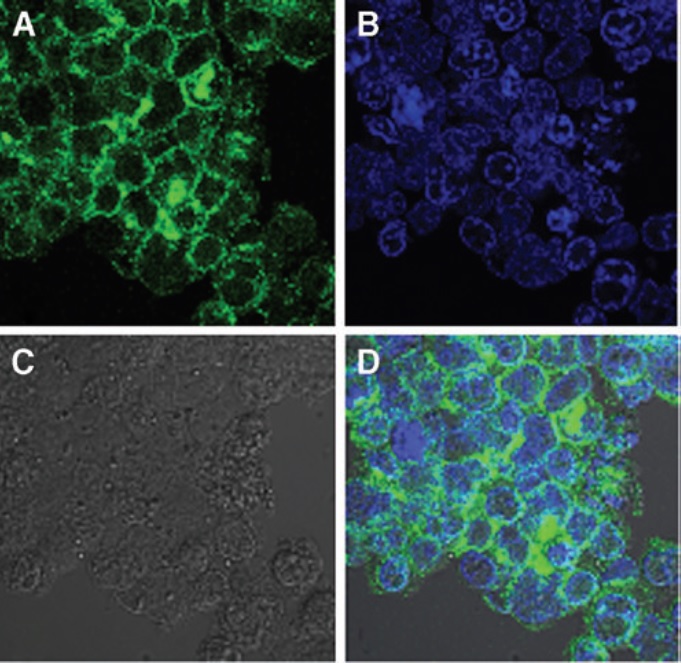
Visual representation for the detection of HCV NS5A protein in infected PBMCs (A) Emission of Green fluorescence is of HCV NS5A. (B) Blue signal is of DAPI used for staining the nuclei of cells. In (C) black and white format of the image is shown, whereas (D) shows the overall emission spectra for HCV NS5A (green) and nuclei of cells (blue).
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection is a major health concern worldwide. The presence of both HCV viral RNA and NS5A proteins in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) indicate the efficacy of the treatment during sustained virological response (SVR) and end of treatment response (ETR). The main objective of this study was to detect the absence or presence of HCV RNA and NS5A proteins in PBMCs. Blood samples were taken from selected patients (Islamabad, Pakistan) before treatment, at ETR, and during SVR. Two hundred HCV responders to pegylated IFN-α-2a plus ribavirin were selected. HCV RNA was extracted from the patients to determine the viral load by reverse transcription (RT)-polymerase chain reaction before treatment. Out of 200 patients, 152 (76 %) and 48 (24 %) achieved positive and negative ETR, respectively. Among ETR patients, 134 (88.2 %) showed SVR, whereas 18 (11.8%) displayed relapse. The male to female ratio was 92:108 with mean age of 37.4 years. Among 152 ETR-positive patients, 29 (19 %) patients’ PBMCs were positive for HCV RNA and 27 (17.8 %) were positive for NS55A proteins. Patients having HCV RNA in PBMCs showed higher relapse frequency compared with patients lacking it. Similarly, patients having NS5A protein showed significantly higher relapse frequency compared with patients lacking it. All PBMC-positive samples were of genotype 3a. In addition, patients with positive NS5A in their PBMCs showed greater risk of relapse compared with patients having HCV RNA. We conclude that the absence of both viral HCV and proteins can be used as an indicator for diagnosis of SVR in the future. [Viral Immunology, 2017]; [Health Security, 2017]. Furthermore, in another related project we evaluated the Temporal Virological Responses to Interferon-α-2b plus Ribavirin among Genotype 3a Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients. [Intervirology, 2017]; [Medicine, 2016]
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Drug Blended Biosynthesized Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles
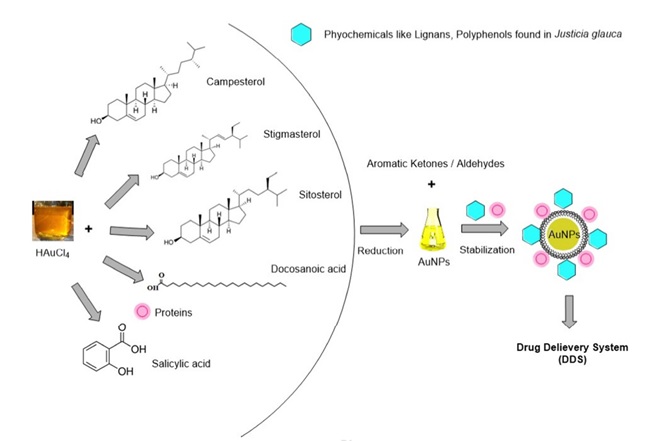
Antimicrobial resistance is a challenging task for researchers to develop new strategies. Green synthesis of AuNPs is an eco-friendly approach, which can be utilized in the microbistatic and microbicidal activities. The current study is focused on Justicia glauca (aqueous leaf extract) mediated AuNPs synthesis at room temperature by treating chloroaurate ions, that shows an antagonistic effect with Azithromycin (AZM) and Clarithromycin (CLR) antibiotics against oral pathogenic bacteria and fungi (Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans). Characterization of green synthesized AuNPs was done by using Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis and Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX). Biosynthesized AuNPs were stable, hexagonal and spherical shaped with a size 32.5 ± 0.25 nm. The AuNPs and drug conjugated AuNPs showed potential antibacterial and antifungal activity against the oral pathogens. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) values of biogenic AuNPs were observed in the range of 6.25-25 μg/mL against selected oral pathogens. Overall, we conclude that biogenic drug delivery system for AZM and CLR can be exploited as potential antimicrobial therapy in future, subject to detailed in-vitro and in-vivo cytotoxicity. [Microbial Pathogenesis, 2017]; [International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018]; [Chemical Research in Toxicology, 2020].




